2.4. Paho MQTT Library¶
We will be using Paho Python library which basically implements a client class that can be used to add MQTT support to your Python program either by creating instances of the client or through inheriting with your own class. It also provides some helper functions to make publishing one shot messages extremely easy.
2.4.1. Installation Instruction¶
Firstly you have to install paho-mqtt library. For that run the following command in your terminal.
pip install paho-mqtt
Note
We need to install paho-mqtt for Python 2.7 and not Python 3.
Establishing connection with the MQTT broker. In our case broker is HiveMQ broker, let’s how to connect.
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt broker_url = "broker.mqttdashboard.com" broker_port = 1883 client = mqtt.Client() client.connect(broker_url, broker_port)
- In above code snippet we imported the paho library and set the broker address url as broker.mqttdashboard.com and port as 1883. Note that for port 1883 is default MQTT port.
- We created a MQTT client object and assigned it to variable client and using client.connect(broker_url, broker_port) we connect() to the broker, if the connection is successful return will be 0.
- The Client() constructor as well as connect() function as following optional parameters as shown below:
mqtt.Client(client_id=””, clean_session=True, userdata=None, protocol=paho.MQTTv31)
where if client_id is not specified by the user, a random id is generated, clean_session must be True always, userdata parameter can be any value or datatype that you wish and the data will be passed to all callbacks as the userdata variable .
client.connect(host=”localhost”, port=1883, keepalive=60, bind_address=””)
where except bind_address rest are obvious, the bind_address which allows the socket to be bound to a specific address at the local side of the connection.
To check if the message has been successfully published to a topic we need a client subscribed to that topic. For this we will write subscribe() function in the script which as shown below
client.subscribe("HiveMQ/pub&sub", qos=0)
where topic and qos is same as discussed above.
Python script to subscribe a topic is given below:
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt broker_url = "broker.mqttdashboard.com" broker_port = 1883 client = mqtt.Client() client.connect(broker_url, broker_port) client.subscribe("HiveMQ/pub&sub", qos=0)
To check the messages on the terminal we will use callback functions.
Callbacks are functions that are executed when an event occurs. In paho these events are connect, disconnect, subscribe, unsubscribe, publish, message received, logging.
Looping functions : It is function of the same client object. When a message is received by the client it is stored in receive buffer and whenever a message is to be sent from client to broker it is stored in send buffer. Now what the loop function does is they are made to process the messages in the respective buffer and call a callback function. There are 3 loop functions as follows.
client.loop_forever()which means the loop function will keep running and you cannot execute any other line after you call this function.client.loop_start()which means you can call this function and still continue executing code after the function call.client.loop_stop()which stops the background thread.
on_connect callback: It is called everytime when a client establishing a connection with the broker. It takes in 4 parameters those are client which is nothing but our client object, userdata is the custom data declared in the client object which is needed if we want to pass custom data into the callback, flags is a dictionary object, used to check if we have set clean session to True or False for the client object and finally rc is the result code, which checks the connection status.
on_message callback: This callback function is used to display the messages those are subscribed to a topic.
It’s alot of theory. Now let’s create a MQTT client by creating two python script namely sub.py (Receiving client) and pub.py (Publishing client).
2.4.2. Example MQTT Pub-Sub¶
2.4.2.1. sub.py¶
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
broker_url = "broker.mqttdashboard.com"
broker_port = 1883
def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc):
print("[INFO] Connected With Result Code: " + str(rc))
def on_message(client, userdata, message):
print("--- Subscriber ---")
print("[INFO] Topic: {}".format(message.topic) )
print("[INFO] Message Recieved: {}".format(message.payload.decode()))
print("------------")
sub_client = mqtt.Client()
sub_client.on_connect = on_connect
sub_client.on_message = on_message
sub_client.connect(broker_url, broker_port)
sub_client.subscribe("/eyrc/vb/time", qos=0)
sub_client.loop_forever()
print("Out of Loop. Exiting..")
2.4.2.2. pub.py¶
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
broker_url = "broker.mqttdashboard.com"
broker_port = 1883
def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc):
print("[INFO] Connected With Result Code: " + str(rc))
def on_message(client, userdata, message):
print("--- Subscriber ---")
print("[INFO] Topic: {}".format(message.topic) )
print("[INFO] Message Recieved: {}".format(message.payload.decode()))
print("------------")
sub_client = mqtt.Client()
sub_client.on_connect = on_connect
sub_client.on_message = on_message
sub_client.connect(broker_url, broker_port)
sub_client.subscribe("/eyrc/vb/time", qos=0)
sub_client.loop_forever()
print("Out of Loop. Exiting..")
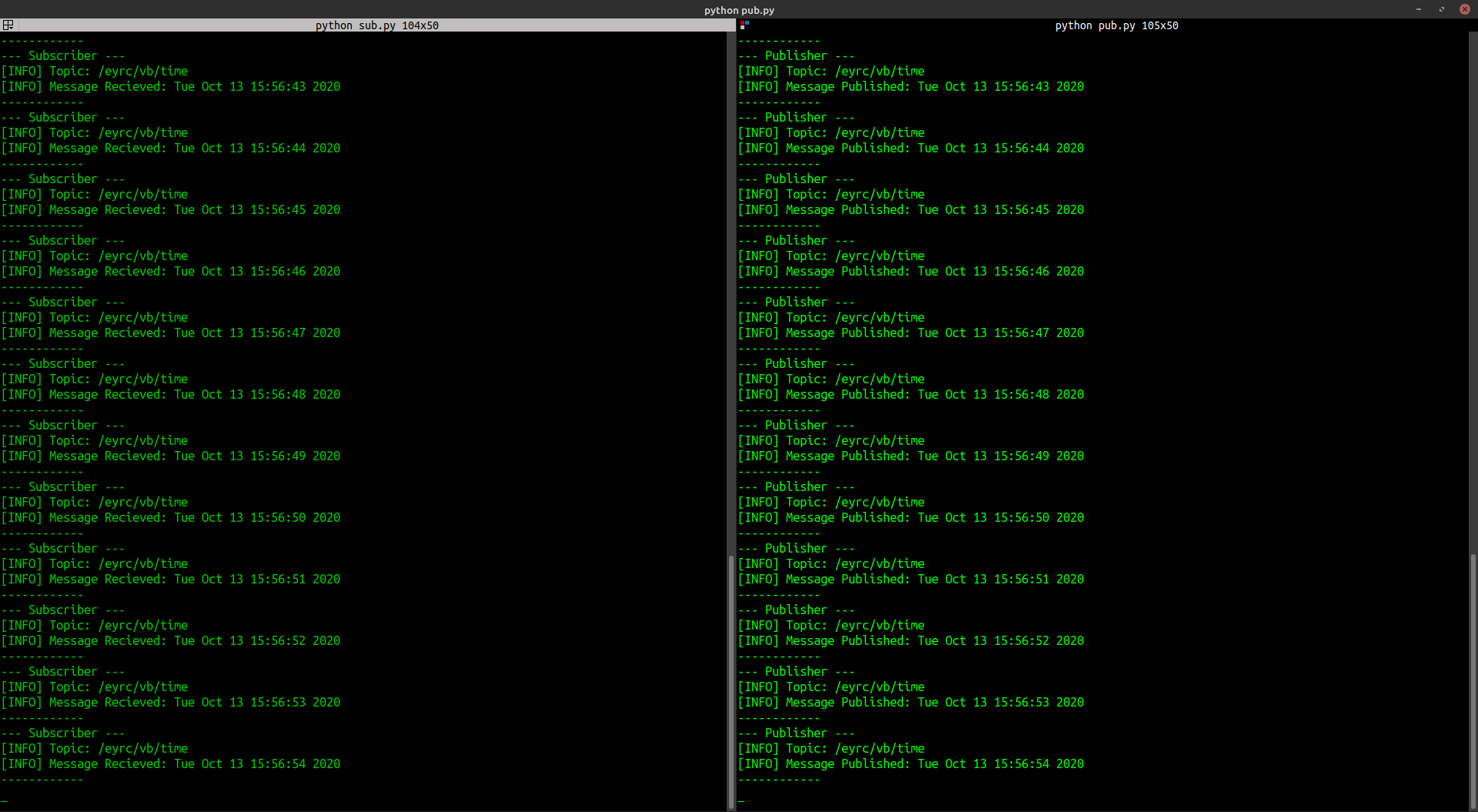
For proper output open two windows of terminal. In first, window run sub.py and in second window run pub.py. The output should look like this.